No products in the cart.

UTI Symptoms and its Treatment
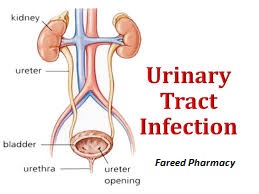
UTI Symptoms and its Treatment: Every year, millions suffer from urinary tract infections (UTIs), one of the most frequent bacterial infections. Bladder, urethra, and kidney infections are all possible locations. A UTI is an infection of the urinary tract. Urinary tract infections (UTIs) occur when bacteria enter the urinary tract through the urethra. These germs typically originate in the skin or rectum. UTIs affect up to 60% of women at some point, although only 40% of men will ever get one. Genetics, sexual activity, gender, and even some drugs can all play a role in causing urinary tract infections. Thankfully, urinary tract infections (UTIs) are usually curable with drugs and other medical procedures.
What Causes UTIs?
Typically, Escherichia coli (E. coli) bacteria are to blame for urinary tract infections (UTIs). These bacteria can reside in the digestive system or on the skin before entering the urethra and making their way to the urine system. Other bacteria, such as Klebsiella, Proteus, Pseudomonas, and Enterococcus faecalis, can also lead to UTIs.
Factors that increase the risk of developing UTIs include:
1. Gender: UTIs are more common in women due to their shorter urethra, which makes it easier for bacteria to reach the bladder.
2. Sexual activity: Sexual activity can introduce bacteria into the urinary tract, increasing the risk of UTIs.
3. Age: Older adults are more susceptible to UTIs as their immune system weakens with age.
4. Genetics: Some people may have genetic factors that make them more prone to UTIs.
5. Catheter use: Urinary catheters can increase the risk of UTIs, as the catheter can introduce bacteria into the bladder.
6. Health conditions: Certain health conditions, such as diabetes, kidney stones, and spinal cord injuries, can increase the risk of UTIs.
Symptoms of UTIs:
Common symptoms of UTIs include:
- A frequent need to urinate
- A burning sensation while urinating
- An urgency to urinate
- Cloudy, strong-smelling urine
- Blood in the urine
- Lower abdominal pain or discomfort
- Fever or chills
Patients may also experience back discomfort, nausea, and vomiting in severe cases. Although urinary tract infections (UTIs) can be uncomfortable and disruptive, medications can usually cure them.
Treatment of UTIs:
If a UTI is suspected, a doctor will typically perform a urine test to confirm the diagnosis. Once diagnosed, UTIs are treated with antibiotics to kill the bacteria causing the infection. The type of antibiotic prescribed will depend on the type of bacteria causing the infection, and treatment duration can range from a few days to two weeks.
While antibiotics are the most common treatment for UTIs, other interventions can also be helpful, including:
1. Pain relief: Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen can help alleviate the pain and discomfort associated with UTIs.
2. Drinking fluids: Drinking plenty of fluids, especially water, can help flush out bacteria from the urinary tract.
3. Warmer compresses: Applying a warm compress to the lower abdomen can help alleviate pain.
4. Cranberry juice: Drinking cranberry juice can help prevent UTIs in some people, but it should not be relied on as the sole treatment.
Prevention of UTIs:
While UTIs cannot always be prevented, there are several steps you can take to reduce your risk of developing one:
- Drinking plenty of water to flush out bacteria from the urinary tract.
- Peeing after sex, which can help flush out bacteria introduced during sex.
- Wiping front to back after using the bathroom to avoid spreading bacteria from the anus to the urethra.
- Avoiding douches and other feminine hygiene products, which can introduce bacteria into the urinary tract.
- Avoid tight-fitting clothing or underwear, which can create a moist environment that bacteria thrive in.
Conclusion:
Infections of the urinary system are frequent and painful but also curable. Although several things, such as heredity and other illnesses, might increase your risk of acquiring a urinary tract infection (UTI), you can take measures to decrease that risk. Urinary tract infections (UTIs) can lead to serious problems if left untreated for too long. Most cases of UTI are curable with appropriate treatment and seldom result in long-term problems.



1,679 Comments